Multiple myeloma
Abstract:
Multiple myeloma belongs to the lymphoproliferative syndromes of the B-cell type. A malignant proliferation of plasma cells is present in the bone marrow. The malignant plasma cells usually secrete an IgG- or IgA-monoclonal immunoglobulin or immunoglobulin fragment (M-protein, M=monoclonal). In 10% of the cases, free light chains are excreted in the urine (Bence-Jones protein). Typically osteolytic lesions and/or diffuse osteoporosis occur. Multiple myeloma constitutes 10-15% of hematological malignancies and usually occurs in older people (rarely under age 40.)
Clinical picture:
Two thirds of the patients complain of joint pain, typically in the back or chest. In advanced stages, pathological fractures can occur. The plasma cell proliferation in the bone marrow causes symptoms of anemia and thrombocytopenia. A tendency toward infection is determined primarily by a decrease in the normal immunoglobulins. Renal failure is mostly determined by the deposition of light chains into the renal tubules. Hypercalcemia can also exacerbate loss of kidney function.
Hematology:
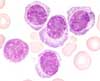 Increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is typical. Rouleau formation of erythrocytes can occur in the blood film. Normochromic-normocytic anemia is usually present. Thrombocytopenia and neutropenia usually reflect the degree of bone marrow infiltration. In rare cases, plasma cells emigrate into the peripheral blood. This is known as plasma cell leukemia.
Increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is typical. Rouleau formation of erythrocytes can occur in the blood film. Normochromic-normocytic anemia is usually present. Thrombocytopenia and neutropenia usually reflect the degree of bone marrow infiltration. In rare cases, plasma cells emigrate into the peripheral blood. This is known as plasma cell leukemia.
Bone marrow:
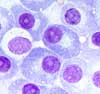 Bone marrow examination, along with serum protein electrophoresis and skeletal surveys, are the main tests for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. An infiltration of plasma cells of over 30% in the bone marrow with osteolytic lesions or M-protein > 30 g/L is diagnostic. If only a 10-30% marrow plasmacytosis exists, both additional criteria must be fulfilled.
Bone marrow examination, along with serum protein electrophoresis and skeletal surveys, are the main tests for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. An infiltration of plasma cells of over 30% in the bone marrow with osteolytic lesions or M-protein > 30 g/L is diagnostic. If only a 10-30% marrow plasmacytosis exists, both additional criteria must be fulfilled.
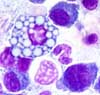 $Sometimes round inclusions can be observed in the plasma cells, the so called Russel-bodies. These contain gammaglobulins. They are also observed in reactive processes with intensive production of immunoglobulins.
$Sometimes round inclusions can be observed in the plasma cells, the so called Russel-bodies. These contain gammaglobulins. They are also observed in reactive processes with intensive production of immunoglobulins.
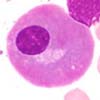 Flaming plasma cells are a rare phenomenom. They mostly occurr in multiple myeloma with an IgA paraproteinemia. $
Flaming plasma cells are a rare phenomenom. They mostly occurr in multiple myeloma with an IgA paraproteinemia. $
Table of Contents
 Increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is typical. Rouleau formation of erythrocytes can occur in the blood film. Normochromic-normocytic anemia is usually present. Thrombocytopenia and neutropenia usually reflect the degree of bone marrow infiltration. In rare cases, plasma cells emigrate into the peripheral blood. This is known as plasma cell leukemia.
Increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is typical. Rouleau formation of erythrocytes can occur in the blood film. Normochromic-normocytic anemia is usually present. Thrombocytopenia and neutropenia usually reflect the degree of bone marrow infiltration. In rare cases, plasma cells emigrate into the peripheral blood. This is known as plasma cell leukemia. Bone marrow examination, along with serum protein electrophoresis and skeletal surveys, are the main tests for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. An infiltration of plasma cells of over 30% in the bone marrow with osteolytic lesions or M-protein > 30 g/L is diagnostic. If only a 10-30% marrow plasmacytosis exists, both additional criteria must be fulfilled.
Bone marrow examination, along with serum protein electrophoresis and skeletal surveys, are the main tests for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. An infiltration of plasma cells of over 30% in the bone marrow with osteolytic lesions or M-protein > 30 g/L is diagnostic. If only a 10-30% marrow plasmacytosis exists, both additional criteria must be fulfilled. $Sometimes round inclusions can be observed in the plasma cells, the so called Russel-bodies. These contain gammaglobulins. They are also observed in reactive processes with intensive production of immunoglobulins.
$Sometimes round inclusions can be observed in the plasma cells, the so called Russel-bodies. These contain gammaglobulins. They are also observed in reactive processes with intensive production of immunoglobulins. Flaming plasma cells are a rare phenomenom. They mostly occurr in multiple myeloma with an IgA paraproteinemia. $
Flaming plasma cells are a rare phenomenom. They mostly occurr in multiple myeloma with an IgA paraproteinemia. $