Primary cytomegalovirus infection (CMV)
Abstract:
The cytomegalovirus (CMV) belongs to the herpes virus family. Primary infection can occur intrauterine (embryopathy) and postnatal conditions (breast feeding), or in adults, through contact with infected saliva, seminal fluid or cervical secretions. The virus remains in the body permanently. Its reactivation occurs in patients with weakened or suppressed immune systems.
Clinical picture:
The clinical picture of a primary cytomegaly infection is very similar to that of mononucleosis, with the exception that pharyngitis is absent. It often occurs asymptomatically. As with mononucleosis, mostly sexually active adolescents are affected. CMV can also be transmitted by blood products containing leukocytes (packed red cells).
Hematology:
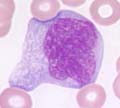
The blood film strongly resembles that of mononucleosis.