Monocytes
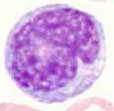
With a diameter of 15 to 20 µm, monocytes are the largest cells in the peripheral blood. Their form is diverse. Monocytes may have pseudo-podi formation on their outer membrane. The cytoplasm is bluish gray. Fine azure granules and vacuoles are often present as well. The nucleus can be bean-shaped or lobulated. Its chromatin is medium fine.
Normal range:
The normal values range from
to
x 109/L. An increase of monocytes is called monocytosis; a dercrease is called monocytopenia.
Function:
Monocytes may have a distinct migration ability. When they have emigrated to the tissue, they are referred to as macrophages. Monocytes take on an important role in acute and chronic infections. They actively phagocytize and are important components of cell-mediated immunity.
Clinical Significance:
Monocytosis is associated with various chronic infections (e.g. tuberculosis, typhoid fever), chronic inflammatory and malignant diseases (e.g. M. Hodgkins). Monocytosis can likewise be found in acute myelomonocytic leukemia and acutemonocytic leukemia as well as in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia.
Monocytopenia is present in bone marrow failure, hairy cell leukemia and in steroid therapy.