Acute HIV infection
Abstract:
In acute (primary) HIV infection, a mononucleosis-like or flue-like clinical picture is observed 8 to 12 weeks after contagion. At this stage, seroconversion occurs. Almost 50% of all HIV-infections go without symptoms. Between contagion and seroconversion lays the serological window., i.e., patients have not formed antibodies yet but can transmit the virus. In order to diagnose HIV-infection at this stage, the antibody test is not sufficient. The diagnosis has to be established by the demonstration of HIV-p24-antigen in the serum and HIV-RNA in plasma via reverse transcription-Polymerase-chain reaction (RT-PCR).
Clinical picture:
The clinical picture is very similar to that of mononucleosis. The possibility of a primary HIV infection must always be considered, especially if the patient engages in activities that could put him/her at risk for contracting the disease. Almost 50% of the patients have no symptoms.
Hematology:
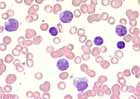
The blood film strongly resembles that of mononucleosis.