Visceral Leishmaniasis
Abstract:
Visceral Leishmaniasis (Kala-Azar) is an infectious disease occurring worldwide in the tropics and the subtropics caused by the protozoan Leishmania donovani. The pathogen is transmitted by sand flies. The not flagellated forms are phagocytosed from macrophages in the bone marrow, the spleen and the liver.
Clinical picture:
Prolonged fever, weakness, weight loss, hepatosplenomegaly, anemia, leukopenia and polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia are typically seen.
Hematology:
Due to splenomegaly, hypersplenism with anemia, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia can develop.
Bone marrow:
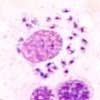
Protozoa can be detected in bone marrow and spleen macrophages. They are round to oval and 1-2 µm in diameter. The nuclei are polymorphic and cytoplasm is palely basophilic.