Megakaryocytes
Definition:
Megakaryocytes develop from megakaryoblasts. They constitute about
of nucleated bone marrow cells (myelogram). A characteristic of megakaryocytic differentiation is nuclear endoreduplication (endomitosis). Active megakaryocytes show a 2 to 16N-ploidy. The function of megakaryocytes is to produce platelets.
Appearance:
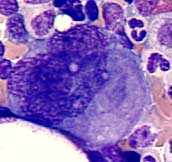
Megakaryocytes are easily recognized, because they are the largest cells that occur in normal bone marrow. They can achieve a diameter of up to 100 µm. The nucleus is also very large and multi-lobated. The cytoplasm is basophilic. In addition, fine azure granules are present.