Plasma cells
Appearance:
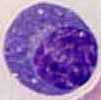
Plasma cells are rarely found in peripheral blood. With a diameter of 15-20 µm, they are larger than lymphocytes. Eccentric nuclei and perinuclear halo are typical features of plasma cells. Unlike the histological preparation, the so-called spoke structure of the nucleus cannot be seen in the aspirate.
Normal range:
The normal range of plasma cells is
to
x 109/L. Consequently, they are rarely found in the blood film. An increase in the number of plasma cells is called plasmacytosis.
Function:
Plasma cells produce antibodies for defense against infection.
Clinical Significance:
Plasma calls are rarely found in peripheral blood. When they are found, however, it is most often following vaccinations.
Benign plasmacytosis occurs in cases of viral infections such as the German measles. In patients with advanced plasmacytoma, a release of plasma cells into the peripheral blood occurs occasionally. A number of clonal plasma cells above 2 x 109/L is called plasma cell leukemia.