May-Hegglin anomaly
Abstract:
The May-Hegglin anomaly is a rare, autosomal-dominant hereditary anomaly with basophilic RNA-condensates in the cytoplasm of neutrophils (pseudo-Döhle bodies) and thrombocytopenia with giant platelets.
Clinical picture:
Patients are usually asymptomatic. However, hemorrhagic diathesis occurs in a subgroup of patients with platelet dysfunction.
Hematology:
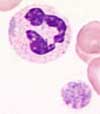
Characteristic are giant platelets and thrombocytopenia. In the cytoplasm of neutrophils and less prominent in monocytes and eosinophils , dirty-blue inclusions are found.