Plasma cells
Definition:
Plasma cells are encountered in bone marrow more often than in the peripheral blood. They constitute about
of nucleated bone marrow cells (myelogram). However, they should not constitute more than 3% of bone marrow cells. Their main function is to produce immunoglobulins for the antibody-defense against infection.
Appearance:
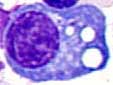
Plasma cells have a coarse, round, eccentric nucleus and basophilic cytoplasm. A perinuclear halo (corresponding to the Golgi apparatus) can usually be identified. Inclusions may be present as well.