Rouleaux formation
Definition:
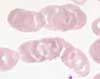
Unlike agglutination, where the erythrocytes clump together, in rouleau formation, the erythrocytes arrange themselves in rows that are reminiscent of rolls of coins. This is also referred to as pseudoagglutination. Rouleau formation occurs in cases of elevated concentrations of high molecular weight plasma proteins, such as gamma globulins. It parallels the accelerated erythrocyte sedimentation rate seen in these conditions.
Occurrence:
In pregnancy (increased fibrinogen), with infections (polyclonal immunoglobulins and fibrinogen are increased) and in multiple myeloma (monoclonal paraproteins).
As an artifact, it is also observed in the case of thick blood films.