Blood picture abnormalities in post-splenectomy
Abstract:
In post-splenectomy as well as in functional asplenia, a series of typical blood picture abnormalities occur.
A splenectomy is a type of treatment used in a series of hematological diseases. Typical are congenital hemolytic anemias (e.g. hereditary spherocytosis, Elliptocytosis) or the otherwise therapy resistant immunothrombocytopenc purpura ITP.
Clinical picture:
Increased vulnerability to bacterial infections, especially to pneumococcal and meningococcal infections, is present. Fulminant sepsis or meningitis may occur.
Hematology:
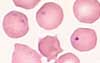
Typical are Howell-Jolly bodies. Their absence proves that there is still some splenic function. If they disappear after splenectomy, formation of an accessory spleen can be assumed. Also typical are Pappenheimer bodies, acanthocytes and target cells. Normoblasts are found to a lesser extent. Lymphocytes, monocytes and platelets are often slightly increased. Directly after the splenectomy, the platelet count can increase temporarily to over 1000 x 109/L.